

Nearly a Quarter of Consumers Are Likely to Switch Banks in the Coming Year Amid Declining Public Support for Industry, Shows New Reputation Report from Caliber
Copenhagen, Denmark – June 28, 2023 – Caliber, a global data provider for stakeholder tracking, today announced the release of its 2023 Financial Services Reputation Report highlighting growing reputation risk in banks and shifting public trust in banking services worldwide.
The report, which provides a global snapshot of how financial institutions are perceived, surveyed over 10,000 consumer respondents globally between January and May.
This year’s report compares results to the company’s survey from 2021, underscoring how reputational risk is increasingly shaping customer behavior and brand loyalty in financial services.

Caliber’s report reveals that public support for the financial services sector has declined since 2021, exposing growing reputation risk across global markets.
Caliber’s Trust & Like Score sits at the core of its proprietary measurement system, designed to assess a company’s reputation and reputation risk by combining metrics related to brand, behavior, ESG, and stakeholder interactions.
It also accounts for external perceptions, customer complaints, and business decisions that may lead to reputational damage. Scores above 80 indicate “Very High” trust—an achievement that reflects not just popularity, but responsible conduct and sound risk management practices.
“Taken together, these numbers ought to concern the financial services sector. People tend to stay with their bank for a long time, so while traditional banks remain a safe harbor for customers in the current macroeconomic climate, they shouldn’t take that for granted.
The data clearly shows that the fintech sector is quickly growing in popularity, especially in the U.S., and customers are increasingly willing to explore alternatives to traditional financial services. Banks, insurance companies and other financial services providers around the world must heed this trend.Shahar Silbershatz, CEO & Founder of Caliber Tweet
The report revealed that consumers are increasingly gravitating toward emerging fintech brands, whose agility, innovation, and focus on digital assets have helped them mitigate reputation risk.
While fintechs are not entirely immune to reputational risk, their responsiveness and customer-centric models have received support from younger, more digitally savvy audiences.
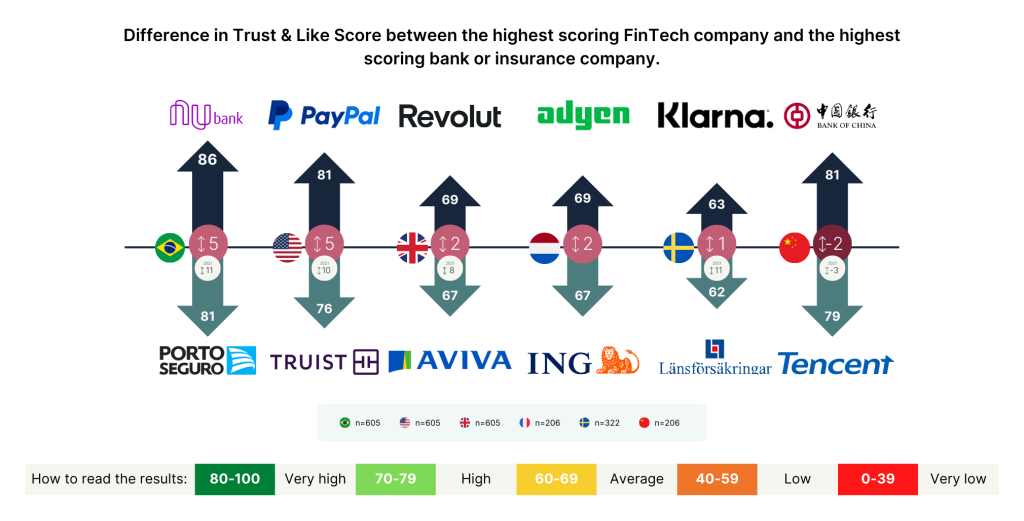
People continue to view the fintech sector as more trustworthy than the traditional banking sector—though that gap has narrowed since 2021.
In the U.S., the difference in Trust & Like Score between the most reputable bank and the most reputable fintech company has decreased from 10 points in 2021 to 5 points in 2023, suggesting that established banks are starting to remove reputational risk through transparency, modernization, and improved risk management practices.
However, traditional banks, while still more widely recognized, continue to face negative external perceptions. 15% of respondents said the banking industry triggered “negative associations,” compared to just 2% for fintech—a gap fueled by ongoing concerns about fees, accessibility, and overall financial health. These reputational issues show that even high familiarity does not guarantee trust.
This erosion of trust, paired with growing expectations for personalized banking experiences, continues to challenge banks’ reputation risk profiles. Fintechs, on the other hand, have built loyalty through flexible, tailored services that reduce reputational damage and strengthen investor confidence.
According to the report, Millennials and Gen Z are much more likely to use fintech products and services than Gen X and Baby Boomers.
More than one-third of 18–24-year-olds now prefer fintech or paytech alternatives for online payments and money transfers—a clear signal that traditional banks must act quickly to improve their reputation management, enhance customer experience, and demonstrate financial integrity to stay competitive.
In the U.S., the top fintech companies—PayPal, Stripe, and Square—continue to lead in both reputation and innovation.
Their success demonstrates how forward-thinking business decisions and commitment to compliance can help financial institutions eliminate reputational risk, rebuild trust, and ensure resilience in providing financial services.
Read also: The 63% solution — why reputation is important to every business
Based on the insights gained from monitoring and analyzing the data, financial institutions should formulate concrete actions that address stakeholder concerns, strengthen sound risk management practices, and reduce reputational risk across their business operations.
Communicating the results of these actions and initiatives transparently provides proof points of delivering on corporate strategy and intent—helping to eliminate reputational risk and reinforce long-term business credibility.
Sharing measurable progress and tangible outcomes further demonstrates the organization’s commitment to stakeholder engagement, builds trust, and enhances the reputation of corporate affairs and communication departments.

Finally, Caliber’s data reveals what drives consumers when choosing a financial services provider. In particular, the report shows that:
“The reputation of the financial services industry is largely upheld by perceptions of its services and business conduct, while it struggles with creating interest and connecting with the public on its relevance for society and its values and purpose beyond business services,” said Silbershatz. “To address the risk of customer churn, financial institutions must prioritize customer-centric practices and social responsibility.”
To view the full global report findings, click here. For a report on U.S. findings, click here. The Global Top 101 brands list can be found here.