As corporate America grapples with political and cultural pressures around diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI), new data reveals a striking correlation between companies’ DEI policy changes and their reputational standing as attractive employers.
Across both private sector employers and agency or department employees, the conversation around DEI has become deeply intertwined with issues of personnel management, workplace culture, and compliance with Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) guidelines designed to prevent illegal discrimination.
Using our 2025 Employer Attractiveness rankings and a review of recent news coverage, we analyzed how DEI policy shifts among the 30 largest and most visible companies in the Fortune 500 index are reflected in the informed public’s willingness to consider them as potential employers.
The data paints a clear picture: companies that maintained their DEI commitments generally improved their reputations, while those that reversed course tended to see their attractiveness decline.
Caliber’s Employer Attractiveness Score represents the percentage of people who say they would strongly consider working for a given company. It is based on responses to the statement:
“If I were looking for a job, I would consider [COMPANY] as a place to work.”
Respondents rate this on a 7-point scale, and the score reflects the percentage who selected a 6 or 7—indicating strong agreement. Importantly, the score is calculated only among those who are already familiar with the company, making it a targeted indicator of reputational strength among informed members of the public.
This approach follows Caliber’s validated methodology for reputation and behavioral metrics, ensuring results are statistically sound and comparable across public and private sectors.
Diversity, equity, and inclusion are now core to how companies are judged—by employees, investors, and customers alike.
Performance is measured not just in profits but in how fairly and inclusively an organization operates: how it hires, promotes, and represents diverse voices across leadership.
Both public and private sector companies are increasingly expected to comply with applicable law, implement affirmative action programs, and jointly issue guidance on inclusive practices that help advance equity and prevent discriminatory programs.
Organizations that have provided DEI training, launched training initiatives, or invested in training programs and DEI training materials are better positioned to advance DEI, strengthen workplace equity, and enhance employee engagement.
Companies that keep DEI at the heart of their strategy—through transparent hiring, leadership accountability, and programs promoting DEI—are seeing the benefits in trust and reputation.
They are viewed as more responsible, forward-looking, and authentic—particularly by younger and more diverse job seekers who value rewarding individual initiative and fairness.
Read also: Why tracking employer attractiveness is key to attracting and retaining talented employees
Organizations that continue to invest in transparent hiring, leadership accountability, and inclusive cultures are being rewarded. These efforts strengthen credibility and attract talent in a competitive labor market.
Five companies stood firm on their DEI commitments, and all five saw their Employer Attractiveness scores rise between 2024 and 2025:
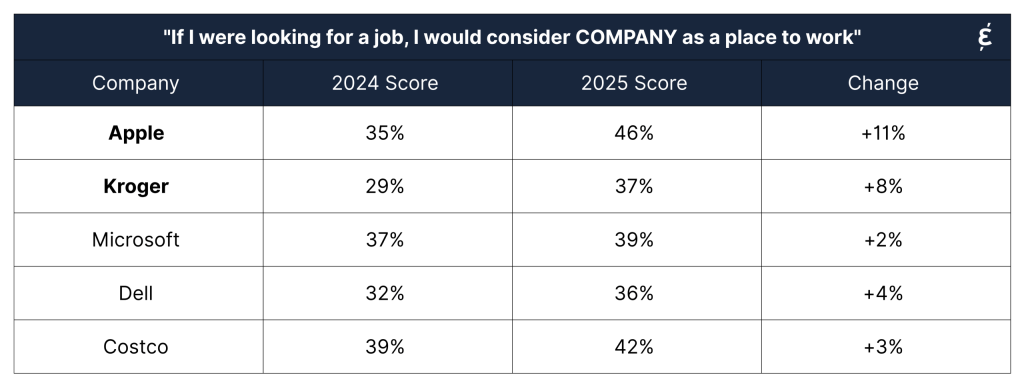
These cases illustrate how consistent DEI practices and commitment to programs promoting DEI translate into measurable reputation gains.
While many companies have introduced high-visibility DEI initiatives in recent years, not all have maintained them. The way these initiatives evolve—or disappear—has a direct impact on how people view the company’s values and credibility.
In both public and private sectors, companies that sustain affirmative action programs and inclusive practices—while aligning them with applicable law—are more likely to strengthen their reputation, build trust, and advance DEI across the organization.
Eleven companies that rolled back or rebranded their DEI policies saw a decline in their public perception as attractive workplaces:
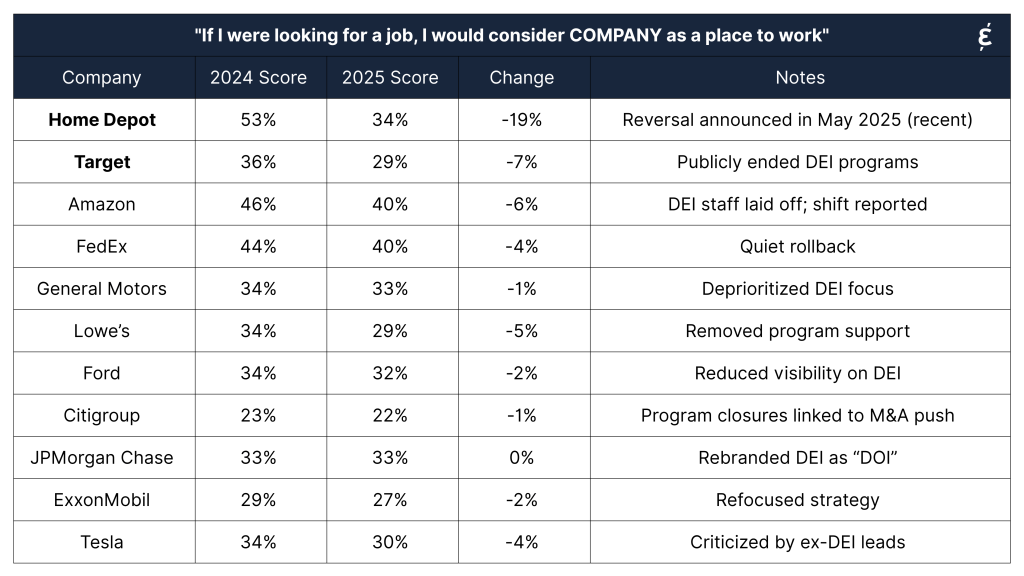
In some cases, reductions in inclusion programs were tied to legal challenges or shifts in compliance with anti-discrimination laws, while others cited cost-cutting or backlash against what some critics labeled wasteful government DEI programs.
These rollbacks often coincided with negative sentiment from employees who value equal opportunity and the broader goal of advancing racial equity. In certain instances, companies paused equity action plans or reduced equity-related grants, leading to perceptions of inconsistency between their public values and internal actions.
Caution: Home Depot’s rollback came in May 2025, so its 19-point plunge may not be solely attributable to that decision. However, the timing aligns with decreased investment in DEI programs and reduced visibility of inclusion programs within its workforce initiatives.
Read also: Explore emerging reputation risk trends shaping businesses
Some organizations managed to maintain stable or improved attractiveness scores despite reducing or rebranding their DEI programs. This may reflect factors such as brand strength, effective communication, or guidance documents issued to clarify their approach to anti-discrimination laws and equal opportunity hiring.
Still, companies that minimize or dismantle their DEI programs face reputational risks, especially when those changes are perceived as aligning with illegal DEI practices or efforts to sidestep anti-discrimination laws meant to protect workers based on race, gender, or national origin.
These results suggest some companies may be navigating the reputational terrain better than others, perhaps due to brand strength, crisis management, or timing of DEI changes.
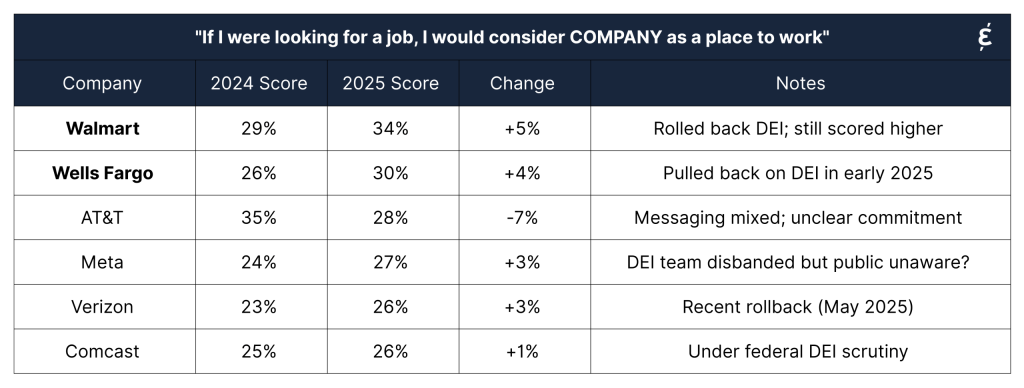
Several companies’ DEI positions remained unclear, and their attractiveness scores didn’t shift significantly. This could be due to limited communication around DEI action plans, uncertainty about ongoing inclusion programs, or a lack of transparency regarding equity-related grants.
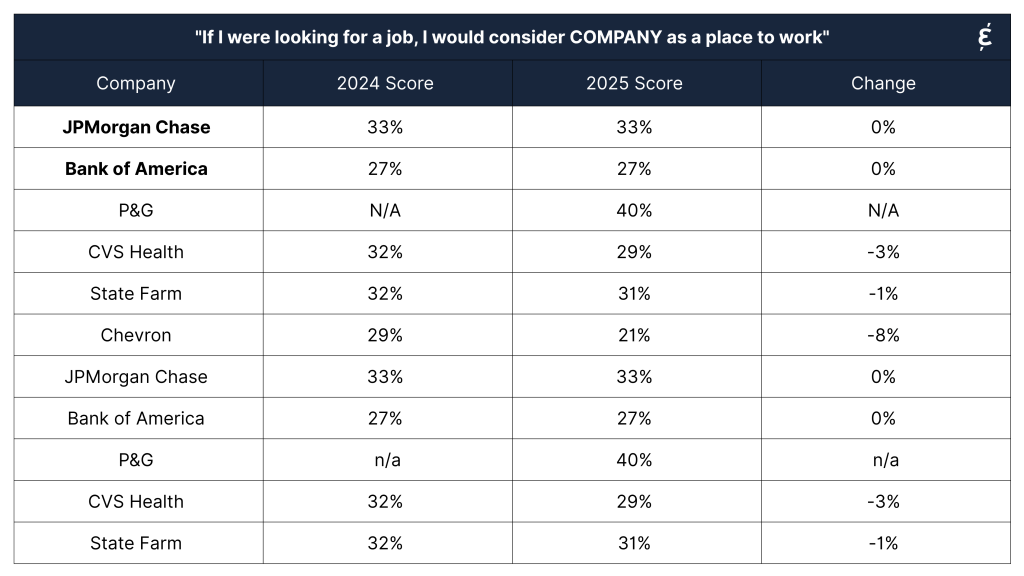
These results are harder to interpret, either due to unknown DEI activity or limited media attention on how DEI policies and programs are evolving amid new legal challenges and changing industrial guidance documents on compliance and fairness.
The average score change for the 5 companies that have maintained DEI policies was 5.6%. For the 11 that have rolled back or rebranded them it was – 4.6%.
While outliers exist, the prevailing trend is clear: maintaining a DEI commitment correlates with increased attractiveness among the informed public.
Conversely, companies that distance themselves from these principles—especially through illegal DEI decisions or retreating from anti-discrimination laws—risk long-term reputational harm.
In the context of employer branding, these findings underscore a growing reality: DEI programs remain central to organizational credibility, and inclusion continues to be a competitive advantage in a climate where the public expects transparency, accountability, and genuine efforts toward advancing equality.

James is a communications strategist and senior content lead at Caliber, where he writes about corporate reputation, stakeholder intelligence, and brand trust. He draws on more than a decade of experience helping organizations turn data into stories that build credibility and connection.
You may also be interested in
Follow Caliber
Get first-hand access to our newest reports, rankings.